CAS number 79-24-3
 General
GeneralSynonyms:
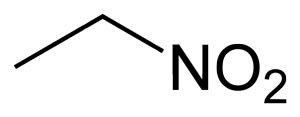
Molecular formula: C2H5NO2
CAS No: 79-24-3
EC No:
Physical data
Appearance: colourless oily liquid with an unpleasant odour
Melting point:
Boiling point: 114 C
Vapour density: 2.6 (air = 1)
Vapour pressure: 15.6 mm Hg at 20 C
Density (g cm-3): 1.05
Flash point: 31 C (closed cup)
Explosion limits:
Autoignition temperature:
Water solubility: slight
Stability
Contact with a variety of materials may cause fire or explosion, especially if heated. Incompatible with amines, strong acids, strong oxidizing agents, combustible materials, metal oxides, strong bases, alkalies.
Toxicology
Harmful if swallowed or inhaled. Typical TLV/TWA 100 ppm. Typical STEL 150 ppm.
Toxicity data :
ORL-RBT LDLO 500 mg kg-1
IPR-MUS LD50 310 mg kg-1
Personal protection
Safety glasses, good ventilation. Do not heat.
Nitroethane is a chemical used mainly as in industrial solvent, fuel additive, propellant, manufacture of pharmaceutical products and in artificial nail removers .
Ingestion and other exposures to the chemical can cause various symptoms. The type and severity of symptoms varies depending on the amount of chemical involved and the nature of the exposure.
Nitroethane is an organic compound having the chemical formula C2H5NO2. Similar in many regards to nitromethane, nitroethane is an oily liquid at standard temperature and pressure.
Pure nitroethane is colourless and has a fruity odor. It is a high volume chemical, with over 1 million pounds of nitroethane being produced.
Nitroethane is produced industrially by treating propane with nitric acid at 350–450 °C. This exothermic reaction produces four industrially significant nitroalkanes: nitromethane, nitroethane, 1-nitropropane, and 2-nitropropane.
The reaction involves free radicals, such as CH3CH2CH2O., which arise via homolysis of the corresponding nitrite ester. These alkoxy radicals are susceptible to C-C fragmentation reactions, which explains the formation of a mixture of products.
 Synonyms/Related:
Synonyms/Related:* Ethane, nitro-
* Nitroetan
* Nitroetan [Polish]
* Nitroethane
* Nitroethane [Flammable liquid]
Properties
Incompatiblities:
o amines
o combustible materials
o hydrocarbons
o metal oxides
o strong acids
o strong alkalis
o strong oxidizers
Health & Regulatory Guidelines
NFPA 704 Rating:
o Health Hazardard Rating
o Fire Hazardard Rating
o Reactivity Hazardard Rating
Benzaldehyde
CAS number 100-52-7
 PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATIONBENZALDEHYDE
EINECS NO. 202-860-4
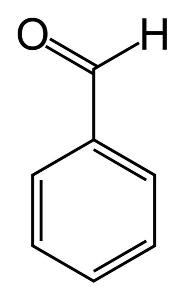
FORMULA C6H5CHO
MOL WT. 106.12
H.S. CODE 2912.21
TOXICITY
Oral rat LD50: 1300 mg/kg
SYNONYMS Benzenecarboxaldehyde; Benzoic aldehyde;
Artificial Almond Oil; Benzenecarbonal; Phenylmethanal; Almond artificial essential oil; Phenylmethanal benzenecarboxaldehyde; Benzadehyde; Benzene carbaldehyde; Phenylmethanal;
DERIVATION CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
PHYSICAL STATE
Colourless to yellow liquid with bitter almonds odor
MELTING POINT -26 C
BOILING POINT 179 C
SPECIFIC GRAVITY 1.044
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
Soluble pH
VAPOR DENSITY
AUTOIGNITION 192 C
NFPA RATINGS Health: 2 Flammability: 2 Reactivity: 0
REFRACTIVE INDEX
1.5450
FLASH POINT
64 C
STABILITY Stable under ordinary conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Benzaldehyde(also called Benzenecarbonal) is the simplest representative of the aromatic aldehydes. It is a colorless liquid aldehyde with a characteristic almond odor. It boils at 180°C, is soluble in ethanol, but is insoluble in water.
Benzaldehyde is formed by partial oxidation of benzyl alcohol and readily oxidized to benzoic acid and is converted to addition products by hydrocyanic acid or sodium bisulfite. It is also prepared by oxidation of toluene or benzyl chloride or by treating benzal chloride with an alkali, e.g., sodium hydroxide. It is used chiefly in the synthesis of other organic compounds, ranging from pharmaceuticals to plastic additives and benzaldehyde is an important intermediate for the processing of perfume and flavouring compounds and in the preparation of certain aniline dyes .
It is the first step in the synthesis for fragrances. It undergoes simultaneous oxidation and reduction with alcoholic potassium hydroxide, giving potassium benzoate and benzyl alcohol.
It is converted to benzoin with alcoholic potassium cyanide, with anhydrous sodium acetate and acetic anhydride, giving cinnamic acid. Compounds which do not have alpha-hydrogen atoms cannot form an enolate ion and do not undergo electrophilic alpha-substitution and aldol condensation.
Aromatic aldehydes such as benzaldehyde and formaldehyde may undergo disproportionation in concentrated alkali (Cannizaro's reaction); one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to the corresponding alcohol and another molecule is simultaneously oxidized to the salt of a carboxylic acid. The speed of the reaction depends on the substituents in the aromatic ring. Two different types of aldehydes (aromatic and aliphatic) can undergo crossing reaction to form fomaldehyde and aromatic alcohols.
SALES SPECIFICATION
APPEARANCE
Clear to yellow liquid
ASSAY 99.0% min
TOLUENE 0.1% max
CHLORINE 20ppm max
ACIDITY 0.5% max (as Benzoic Acid)
BOILING POINT 177-182 C
RELATIVE DENSITY 1.041 - 1.043 at 20 C
Stability
Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, reducing agents, steam. Air, light and moisture-sensitive.
Toxicity data
(The meaning of any abbreviations which appear in this section is given here.)
ORL-RAT LD50 1300 mg kg-1
SCU-RAT LDLO 5000 mg kg-1
SCU-RBT LD50 5000 mg kg-1
ORL-GPG LD50 1000 mg kg-1
3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl-2-propanone
CAS number [4676-39-5]
Identifiers
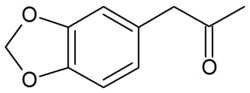
Molecular formula C10H10O3
CAS number [4676-39-5]
SMILES CC(=O)Cc1ccc2OCOc2c1
Properties
Molar mass 178.185 g/mol
3,4-methylenedioxy-phenyl-2-propanoneis a chemical compound consisting of phenylacetone substituted with a methylenedioxy functional group.
It is a chemical precursor of MDA, MDMA (more commonly known as "Ecstasy" or "XTC"), MDEA and related chemicalsMDP2P is most commonly synthesized by oxidizing the plant oil safrole or its isomer isosafrole using the Wacker oxidation or peroxyacid oxidation.
3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-propanone (MDP-2-P or PMK) was prepared by two different routes, i.e. by oxidizing isosafrole in an acid medium and by 1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-nitropropene reduction.
The final product-MDP-2-P was subjected to GC/MS analysis.
The intermediates and reaction by-products were identified and the ‘route specific’ impurities were established.
3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)butan-2-amine (MDP-2-MB, MBDB) is a new homologue of N-methyl-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propan-2-amine (MDMA), which is strictly controlled as a narcotic.
As part of our continuous survey on illegal designer drugs in the Japanese market, we found that N-methyl-4-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)butan-2-amine (MDP-3-MB, HMDMA) was being sold as MBDB.
As this is the first time that HMDMA has been revealed to be in market distribution, and its physico-chemical data is thus far unreported, we describe the structure elucidation of HMDMA and comparative analysis with related compounds.
The impurity profiles were obtained by means of GC/MS, some reaction by-products were identified by means of the EI mass spectra including low energy EI mass spectra and ‘route specific’ impurities were established. 4-Methyl-5-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-[1,3]dioxolan-2-one (compound 22, Table 2), N-methyl-2-methoxy-1-methyl-2-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-ethaneamine (compound 18, Table 2), 3-methyl-6,7-methylenedioxyisoquinoline-1,4-dione (compound 15, Table 1) and N-cyclohexyloacetamide (compound 3, Table 1) were found to be the synthesis markers of greatest importance.
Pseudoephedrine
CAS number 90-82-4
 Systematic (IUPAC) name
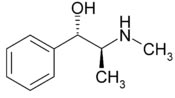
Systematic (IUPAC) name(1S,2S)-2-methylamino-1-phenylpropan-1-ol
Identifiers
CAS number 90-82-4
ATC code R01BA02
PubChem 7028
DrugBank APRD00634
ChemSpider 6761
Chemical data

Formula C10H15NO
Mol. mass 165.23
Pharmacokinetic data
Bioavailability unknown
Metabolism hepatic (10–30%)
Half life 9–16 hours
Excretion 70-90% renal
Pseudoephedrine is a decongestant that shrinks blood vessels in the nasal passages. Dilated blood vessels can cause nasal congestion (stuffy nose).
Pseudoephedrine is used to treat nasal and sinus congestion, or congestion of the tubes that drain fluid from your inner ears, called the eustachian (yoo-STAY-shun) tubes.
Important information about pseudoephedrine
Always ask a doctor before giving a cough or cold medicine to a child. Death can occur from the misuse of cough and cold medicines in very young children. Do not use any other over-the-counter cough or cold medication without first asking your doctor or pharmacist. If you take certain products together you may accidentally take too much of a certain drug. Read the label of any other medicine you are using to see if it contains pseudoephedrine. Do not use a cough or cold medicine if you have used an MAO inhibitor such as isocarboxazid (Marplan), phenelzine (Nardil), rasagiline (Azilect), selegiline (Eldepryl, Emsam), or tranylcypromine (Parnate) within the past 14 days. Serious, life-threatening side effects can occur if you take cough or cold medicine before the MAO inhibitor has cleared from your body.
Pseudoephedrineis a sympathomimetic amine commonly used as a decongestant. The salts pseudoephedrine hydrochloride and pseudoephedrine sulfate are found in many over-the-counter preparations either as single-ingredient preparations, or more commonly in combination with antihistamines, paracetamol (acetaminophen) and/or ibuprofen. Sudafed is a trademark for a common brand which contains pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, though Sudafed PE does not. Cirrus contains Pseudoephedrine in conjunction with Cetirizine (an antihistamine).The advantage of oral pseudoephedrine over topical nasal preparations, such as oxymetazoline, is that it does not cause rebound congestion (rhinitis medicamentosa); however, it is more likely to cause adverse effects including hypertension.
Clinical uses
Indications
Pseudoephedrine is indicated for the treatment of:
* nasal congestion
* sinus congestion
* Eustachian tube congestion.
Pseudoephedrine is also indicated for vasomotor rhinitis, and as an adjunct to other agents in the optimum treatment of allergic rhinitis, croup, sinusitis, otitis media, and tracheobronchitisPseudoephedrine is also used as first-line therapy of priapism. Erection is largely a parasympathetic response, so the sympathetic action of pseudoephedrine may serve to relieve this condition.
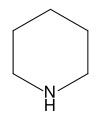
Piperidine
CAS number 110-89-4
General
Synonyms: hexahydropyridine, pentamethyleneimine, azacyclohexane, cyclopentimine, cypentil, hexazane,
Molecular formula: C5H11N
CAS No: 110-89-4
EINECS No: 203-813-0
Annex I Index No: 613-027-00-3
 Physical data
Physical dataAppearance: colourless liquid with the odour of pepper
Melting point: -11 C
Boiling point: 106 C
Vapour density: 3 (air = 1)
Vapour pressure: 40 mm Hg at 20 C
Density (g cm-3): 0.86
Flash point: 16 C (closed cup)
Explosion limits:
Autoignition temperature:
Water solubility: soluble
Stability
Stable. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, organic acids, water. Vapours may flow along surfaces to a distant source of ignition.
Toxicology
Poison. May be fatal if inhaled or swallowed. Severe irritant. Skin contact may cause severe irritation or burns. Contact with the eyes may lead to permanent damage.
Toxicity data
ORL-RAT LD50 400 mg kg-1
IPR-MUS LD50 50 mg kg-1
SKN-RBT LD50 320 mg kg-1
ORL-MUS LD50 30 mg kg-1
ORL-RBT LD50 145 mg kg-1
Risk phrases
R11 R23 R24 R34. (Note: The risk phrases here are those given by Annex I. Annex I does not specify R22 or R25, but this material is clearly harmful if swallowed so should be treated as though R22 were included.]
Personal protection
Safety glasses, gloves, good ventilation. Remove sources of ignition from the working area.
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene units and one nitrogen atom. It is a colorless fuming liquid with an odor described as ammoniacal, pepper-likethe name comes from the genus name Piper, which is the Latin word for pepper. Piperidine is a widely used building block and chemical reagent in the synthesis of organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals.
a colorless, liquid hydrocarbon, (CH)NH, found in many alkaloids and obtained by reducing pyridine or by treating piperine with alkali: used in making rubber, oils, fuels, etc.
Production
Industrially, piperidine is produced by the hydrogenation of pyridine, usually over a molybdenum sulfide catalyst
Production
Industrially, piperidine is produced by the hydrogenation of pyridine, usually over a molybdenum sulfide catalyst
Uses
Piperidine is used as a solvent and as a base. The same is true for certain derivatives: N-formylpiperidine is a polar aprotic solvent with better hydrocarbon solubility than other amide solvents, and 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine is highly sterically hindered base, useful because of its low nucleophilicity and high solubility in organic solvents.
Phosphorus
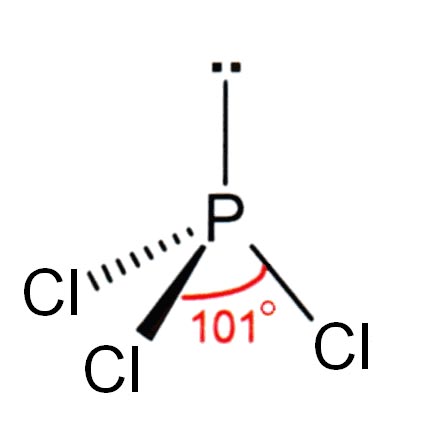
CAS number 7723-14-0

PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
PHOSPHORUS
EINECS NO. 231-768-7
FORMULA P4
MOL WT. 123.88
H.S. CODE 2804.70
TOXICITY
Oral rat LD50: 3030 ug/kg
SYNONYMS Phosphorus (white); Phosphorous yellow; Phosphorus (red);
Black Phosphorus; Fosforo Bianco (Italian); Gelber Phosphor (German); Phosphore Blanc (French); Phosphorous (White); P Tetrafosfor (Dutch); Tetraphosphor (German); Violet Phosphorus; Weiss Phosphor (German)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Phosphorus is a nonmetallic chemical element in group 15 (nitrogen family, formerly Va) of periodic table; atomic number 15 atomic mass 30.9738; melting point ca 44.1 C (white); boiling point ca 280 C (white); specific gravity 1.82 (white), 2.34 (red), 2.70 (black); valence -3, +3, or +5 ; electronic config. 2-8-5 or 1s 22s 22p 63s 23p 3.
The phosphorus molecule is composed of four phosphorus atoms, P4. Phosphorus exists in a number of allotropic forms [white (alpha and beta), red, black and/or violet] in the same physical state. White phosphorus is a white to yellow waxy substance which ignites spontaneously in air to form white fumes of phosphorus pentoxide and glows without emitting heat.
Phosphorus is stored underwater as it is extremely poisonous, insoluble in water (but soluble in carbon disulfide). Commercial production of elemental phosphorus is prepared from phosphorite or phosphate rock (apatite, an impure calcium phosphate mineral) reacting with coke and sand or silica pebblesor at high temperatures in an electric furnace.
Calcium silicate is produced as a by-product. White phosphorus is used as a deoxidizing agent in the preparation of steel and phosphor bronze. It is also used in rat poisons and to make smoke screens (by burning) for warfare. When white phosphorus is heated to about 250 C with air absence, it changes into the red phosphorus.
Red phosphorus, a dark redish powder or crystal, does not ignite spontaneously unless heated to 200 C, does not phosphoresce and it is a little less dangerous than white phosphorus. It is used to make matches. Red phosphorus is prepared commercially by heating calcium phosphate with sand and coke in an electric furnace. Black allotrope is obtained industrially by heating at 300 C under pressure with a mercury catalyst. It has a layer structure and is stable.
The major use of phosphorus compounds is in fertilizers, mainly as a mixture called superphosphate (calcium hydrogen phosphate), obtained from phosphate minerals by sulfuric acid treatment; and in nitrophosphates. Phosphorus is burned to make phosphorus pentoxide [phosphorus(V) oxide], a white solid used as a chlorinating agent in organic chemistry, as a drying agent and mainly converted to phosphoric acid used to make phosphates for fertilizers, electro chemical polishing and shaping, electroplating, metal cleaning and pickling in metal treatment by reaction with water. Phosphorus is highly reactive.
A wide range of compounds is formed for uses in detergents, water softeners, pharmaceuticals, dentifrices, and in many other important applications. It forms metal phosphides and covalently bonded phosphorus(III) and phosphorus(V) compounds. Phosphoric acid can combine with certain alkaline elements to form salts called phosphates.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
PHYSICAL STATE a number of allotropic forms
MELTING POINT 44 C (white), 590 C (red)
BOILING POINT 280 C (white), sublimes (red)
SPECIFIC GRAVITY 1.82 (white), 2.34 (red), 2.70 (black)
SOLUBILITY IN WATER insoluble
pH
VISCOSITY VAPOR DENSITY AUTOIGNITION NFPA RATINGS
Health: 3 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 1
REFRACTIVE INDEX FLASH POINT
30 C(white), 260 C(red)
STABILITY
Stable under ordinary conditions
APPLICATIONS
Phosphoric acid, sodium phosphates, calcium, ammonium and potassium phosphates, phosphorus trichloride, pentasulfide and pentoxide.
SALES SPECIFICATION WHITE/YELLOW PHOSPHORUS APPEARANCE
white to straw yellow waxy solid
ASSAY 99.0% min
INSOLUBLES IN DILUTE NITRIC ACID
0.1% max
ACIDITY (H3PO4)
0.2% max
SULFUR
0.1% max
RED PHOSPHORUS APPEARANCE
red to violet amorphosus powder
ASSAY
98.5% min
SOLUBLES IN WATER
1.0% max
WHITE PHOSPHORUS
0.003% max
MOISTURE
0.25% max
ACIDITY (H3PO4)
0.1% max
HAZARD CLASS
4.2, 4.1 UN NO. 1381 (yellow), 1338 (red)
Uses
In recent years, concentrated phosphoric acids, which may contain as much as 70% to 75% P2O5 content, have become of great importance to agriculture and farm production. World-wide demand for fertilizers has caused record phosphate production. Phosphates are used in the production of special glasses, such as those used for sodium lamps.
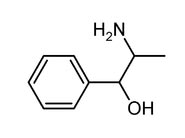
Phenylpropanolamine
CAS number 14838-15-4

Identifiers
Systematic (IUPAC) name (1R,2S)-2-amino-1-phenyl-propan-1-ol
Identifiers
CAS number 14838-15-4
ATC code R01BA01
PubChem 26934
DrugBank APRD00457
ChemSpider 25082
Chemical data
Formula C9H13NO
Mol. mass 151.206 g/mol
Pharmacokinetic data
Half life 2.1 to 3.4 hours.
Therapeutic considerations
Routes Oral
Phenylpropanolamineis a drug ingredient of the phenethylamine family used as a decongestantin prescription and nonprescription (over the counter) cough and cold, and sinus remedies, and some combination allergy medications. It is also present in an appetite suppressant.
Phenylpropanolamine (PPA) is used to treat nasal congestion associated with the common cold, allergies, hay fever, or other respiratory illnesses (e.g., rhinitis, sinusitis). It has also been used as a nonprescription diet-aid for weight loss.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is taking steps to remove phenylpropanolamine (PPA) from all drug products and has requested that all drug companies discontinue marketing products containing PPA. In addition, FDA has issued a public health advisory concerning phenylpropanolamine.
This drug is an ingredient that was used in many over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription cough and cold medications as a decongestant and in OTC weight loss products.
In response to the request made by FDA in November 2000, many companies have voluntarily reformulated and are continuing to reformulate their products to exclude PPA while FDA proceeds with the regulatory process necessary to remove PPA from the market.
Use caution when driving, operating machinery, or performing other hazardous activities. Phenylpropanolamine may cause dizziness or drowsiness. If you experience dizziness or drowsiness, avoid these activities. Never take this medication in larger doses or more often than is recommended. Too much phenylpropanolamine could be very harmful.
Before taking this medication, tell your doctor if you have
* high blood pressure;
* any type of heart disease, hardening of the arteries, or irregular heartbeat;
* thyroid problems;
* diabetes;
* glaucoma or increased pressure in your eye;
* an enlarged prostate or difficulty urinating; or
* liver or kidney disease.
Use caution when driving, operating machinery, or performing other hazardous activities. Phenylpropanolamine may cause dizziness or drowsiness.
If you experience dizziness or drowsiness, avoid these activities. Never take this medication in larger doses or more often than is recommended. Too much phenylpropanolamine could be very harmful.
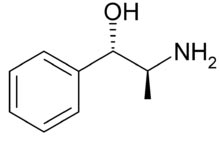
Norpseudoephedrine

CAS number 14838-15-4
 Identification
IdentificationSynonyms Phenylpropanolamine
Molecular Structure Norpseudoephedrine,
Phenylpropanolamine,
Molecular Formula C9H13NO
Molecular Weight 151.21
CAS Registry Number 14838-15-4
EINECS 238-900-2
Closely related to ephedrine, cathinone and other amphetamines, it may contribute to the stimulant effect of Catha edulis, although another constituent, cathinone appears to show stronger activity.
Norpseudoephedrine (1RS,2RS)-2-Amino-1-phenylpropan-1-ole, C9H13NO, MW 151,21 g/mol. The (1S,2S)-Isomer is called Cathine.
Norpseudoephedrine is a scheduled (S2) substance, used as anorexigenic (class A.11.3).
As stimulant, Norpseudoephedrine is included in the doping list of the IOC if a limit value of more than 5 µg/ml in the urine is exceeded.
Norpseudoephedrine is one of the optical isomers of phenylpropanolamine, an appetite suppressant and decongestant which is possibly associated with an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
The World Anti-Doping Agency's list of prohibited substances (used for the Olympic Games among other athletic events) bars cathine in concentrations of over 5 micrograms per milliliter in urine.
Norpseudoephedrine is a Schedule III drug under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances.
In order to investigate effects of khat chewing on uteroplacental blood flow (+) norpseudoephedrine (NPE) infusions were given to 11 anesthetized guinea pigs in late pregnancy (62-66 days) after unilateral uterine artery ligation at days 30-32.
Regional blood flows were determined with radioactive microspheres.
Mean arterial blood pressure increased with 25% and heart rate with 9% during NPE infusion. Myoendometrial blood flow was reduced by 31 %. Placental vascular resistance (PVR) increased by 56% in the control horn (17 fetuses) and by 82% in the ligated horn (17 fetuses).
This vasoconstriction was counteracted by the systemic vasopressor response since placental blood flow remained unchanged. When considering only the 13 growth-retarded fetuses, however, PVR increased by 98% and a 19% reduction of placental blood flow could be demonstrated.
These results suggest that the placenta of the growth-retarded fetus may be more sensitive to adrenergic stimulation than the normal placenta.
Hydroiodic Acid
CAS number 10034-85-2
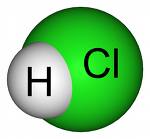
Identifiers
CAS number [10034-85-2]
RTECS number MW3760000
Properties
Molecular formula HI
Molar mass 127.904 g/mol
Appearance Colorless gas.
Density 2.85 g/mL (-47 °C)
Melting point –50.80 °C (184.55 K)
Boiling point –34.36 °C (237.79 K)
Acidity (pKa) –10
Structure
Molecular shape Terminus
Dipole moment 0.38 D
Related compounds
Other anions Hydrogen fluoride
Hydrogen chloride
Hydrogen bromide
Once again, although chemically related, hydroiodic acid is not HI but made from it. Commercial "concentrated" hydroiodic acid usually contains 48% - 57% HI by weight. The solution forms an azeotrope boiling at 127 °C at 57% HI, 43% water. Hydroiodidic acid is one of the strongest of all the common halide acids, despite the fact that the electronegativity of iodine is weaker than the rest of the other common halides. The high acidity is caused by the dispersal of the ionic charge over the anion. The iodide ion is much larger than the other common halides which results in the negative charge being dispersed over a large space. By contrast, a chloride ion is much smaller, meaning its negative charge is more concentrated, leading to a stronger interaction between the proton and the chloride ion. This weaker H+---I− interaction in HI facilitates dissociation of the proton from the anion .
HI(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + I–(aq) (Ka ≈ 1010)
HBr(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + Br–(aq) (Ka ≈ 109)
HCl(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + Cl–(aq) (Ka ≈ 108)
Appearance Yellow color liquid (57% aqueous solution)
Reactivity It reacts with many metals to generate hydrogen and to form the metal iodides. It acts as a reducing agent on organic compounds.
Specifications
Item ISE Standard JIS K8917-1975 Special Class
Nonvolatile constituents 0.01% max. 0.01% max.
Combustion residue (Sulfate) 0.005% max. 0.005% max.
Hydrochloric acid/ Hydrobromic Acid (as CI) 0.01% max. 0.01% max.
Sulfates (SO4) 0.003% max. 0.003% max.
Phosphates (PO4) 0.001% max. 0.001% max.
Heavy metals (as Pb) 0.001% max. 0.001% max.
Iron (Fe) 0.0005% max. 0.0005% max.
Arsenic (As) 0.0001% max. 0.0001% max.
Free iodine (I) 0.06% max. 0.76% max.
Sulfide
To pass test
Appearance (Slightly red)
Assay A: 56% min. 55 ~ 58%
B: 57% min.
Packaging
Outside packing Special plastic container (20l)
Net weight 30 kg (Sealed with nitrogen gas)
Applications
Reducing agent
Iodide synthesis material
Germicides
Medicines
Preparation of inorganic iodides (KI, NaI, NH4I, AgI, etc.)
Preparation of inorganic iodides (iodobenzoic acids or similar compounds for X-ray contrast intermediates, aliphatic iodides, etc.)
Disinfectant and Sanitizer formulations
Health Hazards
1) Fire and explosion: Non-explosive; Water sprinkling is advised to extinguish fire.
2) Gas generation: HI fumes
3) Others Strong mono-basic acid
First aid
1) Rinse eyes with water immediately.
2) Wash contaminated skin areas with soap and dilute aqueous sodium carbonate solution.
3) When taken orally, wash the stomach a 5% aqueous solution of calcium chloride, and administer a self-containing purgative.
4) Oxygen inhalation, and calcium-rich food have been found effective.
Handling & Storage
1) Tightly seal the container and store in a cool, dark, well ventilated place
2) Use rubber gloves, fully body protection garments and gas mask.
3) Mixing and contact hazardous materials: Alkali metals
Spillage
Diluted with water, then cover spilled hydroiodic acid with sodium bicarbonate or a mixture of soda ash and slaked lime (50 : 50). Mix together, and add water if necessary to produce a slurry. Collect the slurry into a container, and wash contaminated surfaces with a large amount of water.
Ergotamine
CAS number 113-15-5
Ergotamine is an ergopeptine and part of the ergot family of alkaloids; it is structurally and biochemically closely related to ergoline.
It possesses structural similarity to several neurotransmitters, and has biological activity as a vasoconstrictor.
It is used medicinally for treatment of acute migraine attacks (sometimes in combination with caffeine), and to induce childbirth and prevent post-partum haemorrhage.
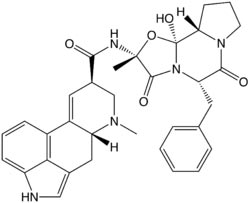
Systematic (IUPAC) name
(6aR,9R)-N-((2R,5S,10aS,10bS)- 5-benzyl-10b-hydroxy-2-methyl- 3,6-dioxooctahydro-2H-oxazolo[3,2-a] pyrrolo[2,1-c]pyrazin-2-yl) -7-methyl-4,6,6a,7,8,9-hexahydroindolo[4,3-fg] quinoline-9-carboxamide
Identifiers
CAS number 113-15-5
ATC code N02CA02
PubChem 9787
ChemSpider 7930
Chemical data
Formula C33H35N5O5
Mol. mass 581.66 g/mol
This belongs to the group of medicines known as Ergot Alkaloids

Ergotamine is used to treat migraine headaches and some other types of throbbing headaches.
Research has shown that migraine can be caused by the swelling of blood vessels around the brain. Ergotamine eases the pain associated with migraine by narrowing these blood vessels.
Ergotamine is available combined with caffeine or other ingredients, in tablet and suppository form.
Ergotamine is in a group of drugs called ergot alkaloids (ER-got AL-ka-loids). It works by narrowing the blood vessels around the brain. Ergotamine also affects blood flow patterns that are associated with certain types of headaches.
Ergotamine is used to treat a migraine type headache.
This medication will only treat a headache that has already begun. It will not prevent migraine headaches or reduce the number of attacks.
Ergotamine should not be used to treat common tension headaches or any headache that seems to be different from your ususal migraine headaches.
How to store Ergotamine
Keep out of reach of children.
Store in a cool, dry place, away from direct light and heat.
Ergonovine
CAS number 60-79-7
 This medication increases uterine contractions resulting in decreased uterine bleeding. It is used to treat or prevent uterine bleeding. It has also been used to treat migraine headaches.
This medication increases uterine contractions resulting in decreased uterine bleeding. It is used to treat or prevent uterine bleeding. It has also been used to treat migraine headaches.Ergonovineis part of a group of medicines called ergot alkaloids. It is used to treat or prevent excessive bleeding after child birth.
General
Synonyms: 9,20-didehydro-N-(alpha-(hydroxymethyl)ethyl)-6-m-ethylergoline-8-beta-carboxamide, ergoline-8-carboxamide, N-((S)-2-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)-lysergamide, ergoatetrine, ergobasine, ergoklinine, ergotocine, ergometrine, ermetrine, margonovine, neofemergen, secacornin, secometrin Use:
Molecular formula: C19H23N3O2
CAS No: 60-79-7
EINECS No: 200-485-0
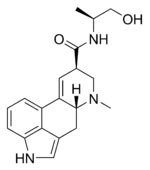 Physical data
Physical dataAppearance: solid
Melting point:
Boiling point:
Vapour density:
Vapour pressure:
Density (g cm-3):
Flash point:
Explosion limits:
Autoignition temperature:
Water solubility:
Stability
Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Toxicology
Toxic if swallowed, inhaled or absorbed through the skin. May cause reproductive damage.
Personal protection
Safety glasses, gloves, good ventilation.
It has a medical use in obstetrics to facilitate delivery of the placenta and to prevent bleeding after childbirth by causing smooth muscle tissue in the blood vessel walls to narrow, thereby reducing blood flow. It is usually combined with oxytocin (syntocinon) as syntometrine.
It can induce spasm of the coronary arteries.
This is sometimes used in the differential diagnosis of angina.
Ephedrine
CAS number 299-42-3
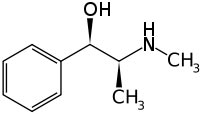 These terms are used to refer to the same substance derived from the plant EphedraEphedra is a shrub-like plant that is found in desert regions in central Asia and other parts of the world. The dried greens of the plant are used medicinally. Ephedra is a stimulant containing the herbal form of ephedrine, an FDA-regulated drug found in over-the-counter asthma medications.Ephedrine alkaloids are amphetamine-like compounds used in OTC and prescription drugs with potentially lethal stimulant effects on the central nervous system and heart. The FDA has received more than 800 reports of adverse effects associated with use of products containing ephedrine alkaloid since 1994. These serious adverse effects, include hypertension (elevated blood pressure), palpitations (rapid heart rate), neurophathy (nerve damage), myopathy (muscle injury), psychosis, stroke, memory loss, heart rate irregularities, insomnia, nervousness, tremors, seizures, heart attacks, and death. The agency has proposed to prohibit the marketing of dietary supplements containing 8 milligrams or more of ephedrine alkaloids per serving.
These terms are used to refer to the same substance derived from the plant EphedraEphedra is a shrub-like plant that is found in desert regions in central Asia and other parts of the world. The dried greens of the plant are used medicinally. Ephedra is a stimulant containing the herbal form of ephedrine, an FDA-regulated drug found in over-the-counter asthma medications.Ephedrine alkaloids are amphetamine-like compounds used in OTC and prescription drugs with potentially lethal stimulant effects on the central nervous system and heart. The FDA has received more than 800 reports of adverse effects associated with use of products containing ephedrine alkaloid since 1994. These serious adverse effects, include hypertension (elevated blood pressure), palpitations (rapid heart rate), neurophathy (nerve damage), myopathy (muscle injury), psychosis, stroke, memory loss, heart rate irregularities, insomnia, nervousness, tremors, seizures, heart attacks, and death. The agency has proposed to prohibit the marketing of dietary supplements containing 8 milligrams or more of ephedrine alkaloids per serving.Systematic (IUPAC) name
(1R,2S)-2-(methylamino)-1-phenylpropan-1-ol
Identifiers
CAS number 299-42-3
ATC code R01AA03 R03CA02 S01FB02
PubChem 5032
DrugBank DB01364
ChemSpider 8935
Chemical data
Formula C10H15NO
Mol. mass 165.23
SMILES eMolecules & PubChem
Pharmacokinetic data
Bioavailability 85%
Metabolism minimal hepatic
Half life 3–6 hours
Excretion 22-99% renal
Therapeutic considerations
Routes oral, IV, IM, SC
 This drug should not be used in combination with other stimulant products (e.g., caffeine), other cough-and-cold products, or as a dietary supplement for the purpose of weight loss or body building. Doing so may increase your risk of unlikely but potentially fatal side effects including: stroke, heart attack, seizures, or severe mental disorders.
This drug should not be used in combination with other stimulant products (e.g., caffeine), other cough-and-cold products, or as a dietary supplement for the purpose of weight loss or body building. Doing so may increase your risk of unlikely but potentially fatal side effects including: stroke, heart attack, seizures, or severe mental disorders.In addition, dietary supplements containing ephedrine should not exceed 8 mg as a single ephedrine dose, 24 mg of ephedrine per day (24 hours), or be given for longer than 7 days, as recommended by the FDA. Exceeding the recommended ephedrine dose increases your risk of the side effects noted above. For detailed information, consult your pharmacist. Check all product labels carefully to see if they contain ephedrine.
USES: Ephedrine is a central nervous system stimulant used to treat breathing problems (as a bronchodilator), nasal congestion (as a decongestant), low blood pressure problems (orthostatic hypotension), or myasthenia gravis.
OTHER USES: This drug has also been used to treat certain sleep disorders (narcolepsy), menstrual problems (dysmenorrhea), or urine-control problems (incontinence or enuresis).
Benzyl Cyanide
CAS number [140-29-4]
![Benzyl Cyanide CAS number [140-29-4]](http://www.tajapi.com/api%20images1/Benzyl-cyanide.jpg)
Identifiers
CAS number [140-29-4]
PubChem 8794
SMILES [show]C1=CC=C(C=C1)CC#N
Stability
Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. May produce hydrogen cyanide in a fire.
Toxicology
Toxic. May be fatal if inhaled. Harmful if swallowed or absorbed through the skin. Readily absorbed through the skin. Eye, skin and respiratory irritant.
General
Synonyms: benzeneacetonitrile, phenyl acetyl nitrile, cyanomethylbenzene, benzyl nitrile
Molecular formula: C8H7N
CAS No: 140-29-4
EINECS No: 205-410-5
Physical data

Appearance: colourless liquid
Melting point: -24 C
Boiling point: 233 C
Vapour density:
Vapour pressure: 0.1 mm Hg at 20 C
Density (g cm-3): 1.015
Flash point: 101 C
Explosion limits:
Autoignition temperature:
Water solubility:
Toxicity data
(The meaning of any toxicological abbreviations which appear in this section is given here.)
ORL-RAT LD50 270 mg kg-1
IHL-RAT LC50 430 mg/m3/2h
SKN-RAT 2000 mg kg-1
ORL-GPG LD50 10 mg kg-1
Transport information
(The meaning of any UN hazard codes which appear in this section is given here.)
Hazard class: 6.1 Packing group: III
Personal protection
Safety glasses, good ventilation, gloves.
Safety phrases
(The meaning of any safety phrases which appear in this section is given here.)
S26 S27 S36 S37 S39.
Anthranilic acid
CAS number 118-92-3
 Anthranilic acid is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)CO2H. This amino acid is white solid when pure, although commercial samples may appear yellow. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with two adjacent functional groups, a carboxylic acid and an amine. Because these two groups are polar, this organic compound is highly soluble in water. It is sometimes referred to as vitamin.
Anthranilic acid is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)CO2H. This amino acid is white solid when pure, although commercial samples may appear yellow. The molecule consists of a benzene ring with two adjacent functional groups, a carboxylic acid and an amine. Because these two groups are polar, this organic compound is highly soluble in water. It is sometimes referred to as vitamin.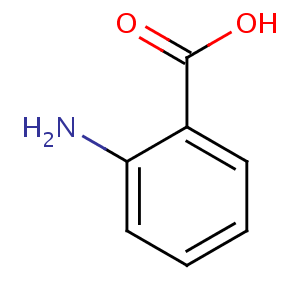
Properties
Molecular formula C7H7NO2
Molar mass 137.14 g mol−1
Density 1.4 g/cm3
Melting point
146-148 °C
Boiling point
Sublimes
Solubility in water 5.7 g/L (25 °C)
Solubility Hot water
Hazards
MSDS External (html)
R-phrases R36 R37
S-phrases S26 S39
Flash point >150 °C
Synonyms:
o-Aminobenzoic acid; 2-Carboxyaniline; Anthranilic acid; Benzoic acid, o-amino-; Kyselina o-aminobenzoova [Czech]; Anthranilate; o-Carboxyaniline; ortho-Aminobenzoic acid; 2-Aminobenzoic acid; ANTHRANILIC ACID; Benzoic acid, 2-amino-; Kyselina anthranilova [Czech]; 1-Amino-2-carboxybenzene; 2-Aminobenzoate; Caswell No. 033G; Vitamin L1; BRN 0471803; o-Anthranilic acid; NCI-C01730; AI3-02408
Uses
Anthranilic acid is used as an intermediate for production of dyes, pigments, and saccharin. It and its esters are used in preparing perfumes to imitate jasmine and orange, pharmaceuticals (loop diuretics eg. furosemide) and UV-absorber as well as corrosion inhibitors for metals and mold inhibitors in soya sauce.
Anthranilic acid can be used in organic synthesis to generate the benzyne intermediate.
| TYPES OF HAZARD / EXPOSURE | ACUTE HAZARDS / SYMPTOMS | PREVENTION | FIRST AID / FIRE FIGHTING |
| FIRE | Combustible. Gives off irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire. | NO open flames. | Powder, water spray, foam, carbon dioxide. |
| EXPLOSION | Finely dispersed particles form explosive mixtures in air. | Prevent deposition of dust; closed system, dust explosion-proof electrical equipment and lighting. | |
| EXPOSURE | | | |
| Inhalation | | Local exhaust or breathing protection. | Fresh air, rest. |
| Skin | | Protective gloves. | Rinse and then wash skin with water and soap. |
| Eyes | Redness. Pain. | Safety spectacles | First rinse with plenty of water for several minutes (remove contact lenses if easily possible), then take to a doctor. |
| Ingestion | | Do not eat, drink, or smoke during work. | Rinse mouth. Give one or two glasses of water to drink. Seek medical attention if you feel unwell |
Denatonium Benzoate
CAS number [3734-33-6]
![Denatonium Benzoate CAS number [3734-33-6]](http://www.tajapi.com/api%20images1/image001.gif) Denatonium Benzoate is the leading bitterant safety additive for household, automotive and garden products worldwide. Consumers recognize Bitrex for its added safety as a taste aversive. The Bitrex Trademark Program is valued by manufacturers for its marketing, technical and regulatory support services. Marketers and retailers recognize the simple concept: "safety sells."
Denatonium Benzoate is the leading bitterant safety additive for household, automotive and garden products worldwide. Consumers recognize Bitrex for its added safety as a taste aversive. The Bitrex Trademark Program is valued by manufacturers for its marketing, technical and regulatory support services. Marketers and retailers recognize the simple concept: "safety sells."He bitterness of the compound guides most applications of denatonium. Denatonium benzoate is used to denature ethanol so that it is not taxed as an alcoholic beverage. One designation in particular, SD-40B, indicates that ethanol has been denatured using denatonium benzoate. The common name for this chemical, denatonium, alludes to this application.
Denatonium also discourages consumption of harmful alcohols like methyl alcohol and ethylene glycol. Denatonium is also used in rubbing alcohol as an inactive ingredient. It is also added to all kinds of harmful liquids including solvents, paints, varnishes, toiletries, and other household products. Denatonium is a quaternary ammonium cation. It is a compound of a salt with an inert anion like benzoate or saccharide. The structure of denatonium is related to the local anesthetic lidocaine, differing only by the addition of a benzyl group to the amino nitrogen.
General
Synonyms: benzyl diethyl ((2,6-xylylcarbamoyl)methyl) ammonium benzoate
Use: animal and bird repellent
Molecular formula: C21H29N2O . C7H5O2
CAS No: 3734-33-6
EINECS No: 223-095-2
Physical data
Appearance: white crystals
Melting point: 166 - 170 C
Boiling point:
Vapour density:
Vapour pressure:
Density (g cm-3):
Flash point:
Explosion limits:
Autoignition temperature:
Water solubility: soluble
Stability
Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Toxicology
Toxic by ingestion. Skin, eye and respiratory irritant. May be harmful by inhalation or if absorbed through skin.
Toxicity data
(The meaning of any toxicological abbreviations which appear in this section is given here.)
ORL-RAT LD50 584 mg kg-1
ORL-RBT LD50 508 mg kg-1
Risk phrases
(The meaning of any risk phrases which appear in this section is given here.)
R25 R36 R37 R38.
Transport information
Personal protection
Safety glasses, adequate ventilation.
Safety phrases
(The meaning of any safety phrases which appear in this section is given here.)
S2 S13 S24 S36 S46.
3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl-2-propanone
CAS number [4676-39-5]

Identifiers
Molecular formula C10H10O3
CAS number [4676-39-5]
SMILES CC(=O)Cc1ccc2OCOc2c1
Properties
Molar mass 178.185 g/mol
3,4-methylenedioxy-phenyl-2-propanoneis a chemical compound consisting of phenylacetone substituted with a methylenedioxy functional group.
It is a chemical precursor of MDA, MDMA (more commonly known as "Ecstasy" or "XTC"), MDEA and related chemicalsMDP2P is most commonly synthesized by oxidizing the plant oil safrole or its isomer isosafrole using the Wacker oxidation or peroxyacid oxidation.
3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-propanone (MDP-2-P or PMK) was prepared by two different routes, i.e. by oxidizing isosafrole in an acid medium and by 1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-nitropropene reduction.
The final product-MDP-2-P was subjected to GC/MS analysis.
The intermediates and reaction by-products were identified and the ‘route specific’ impurities were established.
3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)butan-2-amine (MDP-2-MB, MBDB) is a new homologue of N-methyl-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propan-2-amine (MDMA), which is strictly controlled as a narcotic.
As part of our continuous survey on illegal designer drugs in the Japanese market, we found that N-methyl-4-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)butan-2-amine (MDP-3-MB, HMDMA) was being sold as MBDB.
As this is the first time that HMDMA has been revealed to be in market distribution, and its physico-chemical data is thus far unreported, we describe the structure elucidation of HMDMA and comparative analysis with related compounds.
The impurity profiles were obtained by means of GC/MS, some reaction by-products were identified by means of the EI mass spectra including low energy EI mass spectra and ‘route specific’ impurities were established. 4-Methyl-5-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-[1,3]dioxolan-2-one (compound 22, Table 2), N-methyl-2-methoxy-1-methyl-2-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-ethaneamine (compound 18, Table 2), 3-methyl-6,7-methylenedioxyisoquinoline-1,4-dione (compound 15, Table 1) and N-cyclohexyloacetamide (compound 3, Table 1) were found to be the synthesis markers of greatest importance.
fg
ReplyDeletevery good blog
ReplyDeletegood info
ReplyDeletei use the info one khat
ReplyDeletethanks very mucj :)
Somu Solvents Pvt. Ltd. Provides Ethyl 3 Ethoxypropionate, Ethylene Glycol Diacetate, Ethyl 3 Ethoxypropionate, Ethylene Glycol Diacetate, Butyl Diglycol Acetate, 2 Ethylhexyl Acetate, 1 Methoxy 2 Propanol Propionate Manufacturers in India.
ReplyDeleteSomu Solvents Pvt. Ltd. Provides Ethyl 3 Ethoxypropionate, Ethylene Glycol Diacetate, Ethyl 3 Ethoxypropionate, Ethylene Glycol Diacetate, Butyl Diglycol Acetate, 2 Ethylhexyl Acetate, 1 Methoxy 2 Propanol Propionate Manufacturers in India.
ReplyDeleteSomu Solvents Pvt. Ltd. Provides Ethyl 3 Ethoxypropionate, Ethylene Glycol Diacetate, Ethyl 3 Ethoxypropionate, Ethylene Glycol Diacetate, Butyl Diglycol Acetate, 2 Ethylhexyl Acetate, 1 Methoxy 2 Propanol Propionate Manufacturers in India.
ReplyDeleteSomu Solvents Pvt. Ltd. Provides Ethyl 3 Ethoxypropionate, Ethylene Glycol Diacetate, Ethyl 3 Ethoxypropionate, Ethylene Glycol Diacetate, Butyl Diglycol Acetate, 2 Ethylhexyl Acetate, 1 Methoxy 2 Propanol Propionate Manufacturers in India.
ReplyDeleteBenzalkonium Chloride Manufacturers
ReplyDeleteSomu Group we have been supplying solvents, chemicals, Speciality fine chemicals, intermediates and other Benzalkonium Chloride Manufacturers products to your industry for almost 4 decades.
Nice information shared online!!!
ReplyDelete-------------------------------
Adhesive Manufacturer
Somu group of companies are manufacturers of speciality fine chemicals, pharma intermediates, agrochemical intermediates. We also are Distributors for solvents, stockists of solvents,distributors of packaging products, customised industrial packaging fabrication, in India.
ReplyDeletehttp://www.somugroup.com/